The Science and Ethics behind Halal Gelatin

Gelatin is a protein. It is made mostly from the collagen of cows and pigs. Capsules, cosmetics, ointments, and culinary items are frequently made with it.
Gelatin supplementation may stimulate the body's synthesis of collagen. There isn't enough solid scientific data to back up the numerous other uses of gelatin, including treating obesity, diarrhea, brittle nails, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and aged skin.
What Is Gelatin?
Gelatin is a transparent, flavorless, and colorless food component. It is often made from collagen extracted from animal tissues. When dry, it is brittle. When wet, it becomes rubbery. Gelatin is frequently used as a gelling ingredient in food, drinks, pills, pharmaceuticals, vitamin or medicine capsules, papers, films, and cosmetics.
Boiling animal bones, cartilage, and skin in water yields gelatin. The collagen is broken down into smaller proteins by this process, and the smaller proteins are subsequently dried and powdered. Gelatin is available for purchase in sheets, powder, or granules.
Gelatin is a good source of protein and amino acids. It has low fat and calorie content. Furthermore, it's a great source of glycine.There are various health benefits associated with this particular amino acid. Among them are boosting immunity, reducing inflammatory response, and improving sleep.
Gelatin finds extensive use in several food-related applications. It's used to thicken sauces and soups. It acts as a stabilizing ingredient in yogurt and ice cream. A gelling agent used in desserts like marshmallows and Jell-O. In addition, gelatin is a component of many other goods, including gum, toothpaste, and vitamins.
Importance of Halal certification in food products for Muslims.
The Arabic word "halal" means "lawful" or "permitted." Halal's antithesis, haram, signifies something that is forbidden or illegal. Food goods, meat products, cosmetics, personal care items, medications, food ingredients, and materials that come into touch with food are all included by this word.
The Halal Certificate guarantees that the products have undergone a comprehensive inspection by the relevant body in compliance with Islamic Shariah Laws.
Prior to selling or exporting your goods to Halal purchasers, you must receive this assurance since Halal consumers/buyers would only purchase products certified with the Halal mark.

Based on the information provided above, you would be aware of the goal of Halal certification. You now understand its significance for producers, distributors, exporters, and retailers.
Muslim buyers select goods based on their conformity with Islamic legal definitions of method and procedure. With halal certification, you can sell your goods internationally, mostly in nations with a larger Muslim population.
With this accreditation, you can simply get into the halal market. It helps you to comply with importing countries' requirements when you export products. The greatest markets for halal products are Southeast Asia and the Middle East, where there is a considerable demand for halal-certified goods.
-
The Halal certificate will enable you to comply with one of the crucial standards set forth by the importing countries if you are exporting to or intend to export to countries with a majority of Muslims.
-
A Halal certificate attests to a product's compliance with Islamic dietary laws and lifestyle standards.
-
Halal is suitable for anyone. Whether you practice Islam or not, halal is the gold standard for purity and safety, ensuring goods of the highest caliber. Non-Muslims can also consume halal cuisine, but Muslims can only eat halal food.
Origins and primary sources Of Gelatin:
Animal bones, hides, and skin
Although gelatin is commonly connected to the hooves of many animals, including horses, it is actually a protein found in living beings' bones. The majority of the gelatin that we consume originates from farmed animals like pigs and cows.
Some gelatin brands itself as kosher, indicating that cattle are the only source of its source. To make the necessary gel, the animals' bones and other body parts are cooked.
Scales and fish skin can also be boiled to generate gelatin. The first person known to have made gelatin by boiling animal bones was the Frenchman Denis Papin in 1682.
But even before Papin considered boiling bones, an Arabic cookbook authored in Baghdad in the tenth century by Ibn Sayyar al-Warraq.
Which Animals Are Used to Make Gelatin?
Fish, pigs, and cows are the animals used to make most gelatin. Fish are employed to create the least of these three. The material of interest is obtained by boiling several components of these animals, practically all of which are composed of protein.
Fish skins, pig and cattle bones, and cow and pig skins are a few of them. These animal parts are available at slaughterhouses, either as leftovers from the process of producing meat or after animals have been murdered specifically to make gelatin.
Is Pig Skin Included in Gelatin?
Pig skins and other animal parts from several species are used in the production of many gelatins and gelatin products. Apart from gelatins derived from pig skin or a mix of pig skin and other collagen-producing materials, there are also fish gelatins and gelatins derived only from portions of cattle bodies. Because these gelatins don't include pigs or their components, they are frequently marketed as being compliant with specific religious tenets.
Production Of Hydrolyzed Collagen
Hydrolysis is used to turn partially purified collagen into gelatin. There are three techniques for hydrolyzing collagen: enzymatic, alkali, and acid hydrolysis.
Acid treatment usually takes 10 to 48 hours and is particularly useful for less fully cross-linked materials like collagen from pig skin.
More complicated collagen, such that found in cow skins, responds well to alkali treatment, which takes longer—typically several weeks. The alkali treatment aims to break down some of the remaining chemical crosslinks in collagen.
Within the gelatin industry, type-A gelatin is the gelatin derived from raw materials treated with acid, whereas type-B gelatin is the gelatin derived from raw materials treated with alkali.
Through the enzymatic hydrolysis of collagen, advances are being made to maximize the output of gelatin. The process yields nearly full conversion to the pure product and requires less treatment time than alkali treatment. The finished gelatin product's physical characteristics are thought to be superior.
The subsequent stages comprise the hydrolyzed collagen synthesis process:
Raw material: Collagen derived from animal sources, such as fish bones, pig skins, and cow hides, is usually used as the raw material for hydrolyzed collagen. In order to eliminate contaminants, the collagen is first cleaned and demineralized.
Hydrolysis: After that, the collagen is broken down by acids, enzymes, or a mix of the two. Collagen is hydrolyzed to produce smaller peptides and amino acids.
Neutralization: To correct the pH, the solution is neutralized once the required level of hydrolysis has been reached. Sodium hydroxide is usually used for this.
Filtration: Next, the solution is filtered to get rid of any particles that haven't dissolved.
Concentration: A number of techniques, including evaporation and reverse osmosis, are then used to concentrate the solution. The concentration of the hydrolyzed collagen rises as a result.
Drying: To create a powder or solid form of hydrolyzed collagen, the concentrated solution is subsequently dried.

Some of the variables that may impact the process of producing hydrolyzed collagen include the following:
Raw material type: Depending on the kind of raw material used, the hydrolyzed collagen's yield and quality may change. The collagen derived from cows is of higher quality than that from pigs.
Method of hydrolysis: The technique used to carry out the hydrolysis, affects the yield and quality of the reduced collagen. It is believed that enzymatic hydrolysis is a safer method than acid hydrolysis. A wider range of molecular weights of hydrolyzed collagen can be obtained from it.
The degree of hydrolysis describes the extent to which collagen has fragmented into smaller peptides and amino acids. A higher degree of hydrolysis is indicative of a product that is more bioavailable and soluble.
Drying technique: The hydrolyzed collagen's stability and quality may be impacted by the drying technique employed. For hydrolyzed collagen, spray drying is usually regarded as the optimum drying technique because it maintains the product's activity and bioavailability.
An adaptable component, hydrolyzed collagen can be found in many different food, drink, and nutritional products. It is also a component of many other goods, including medicines and cosmetics.
The Science Behind Halal Gelatin
Gelatin is a special kind of material that is transparent, flavorless, and colorless. The word "halal" signifies "permissible." This indicates that no pig-based products were used in the production of halal gelatin.
This animal is considered unfavorable in the Islamic faith. As a result, it is inappropriate to produce any kind of consumable product using pigs. Furthermore, the animal used to make the gelatin needs to have undergone a killing procedure compliant with Islamic law.
What makes gelatin "Halal"?
Gelatin comes from collagen found in animal bones, skin, and connective tissue. It acts as a stabilizer, thickener, and gelling agent in a lot of food items and beverages. Marshmallows, gummy bears, ice cream, and yogurt contains gelatin.
Gelatin production must also follow halal standards. This implies that the procedure cannot involve the use of any haram materials or pig products.
The Halal Products Research Council (HPRC) and the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America (IFANCA) are two examples of halal certification organizations that frequently certify halal gelatin. These organizations make sure that the production of the gelatin complies with Islamic law.

The following conditions must be met for gelatin to be regarded as halal:
-
A halal animal, such as cattle, lamb, or chicken, must provide the gelatin.
-
Islamic Sharia must be followed before slaughtering the animal.
-
The production of the gelatin cannot involve the use of pork products or any other prohibited materials.
-
A respectable halal certification organization must certify the gelatin.
Halal Sources Of Gelatin
There are several ways to make halal gelatin, including:
Beef: The most prevalent kind of halal gelatin is made from beef. It comes from cattle that have been killed in compliance with Islamic law, and their bones and hides.
Chicken: Another well-liked source of halal gelatin is chicken gelatin. It comes from hens that have been slain in compliance with Islamic law, using their bones and hides.
Fish: Although it's not as widely available as it once was, fish gelatin is a growing source of halal gelatin. It comes from fish that is okay for Muslims to eat, including the bones and skins.
A few sources of gelatin that are derived from plants are also regarded as halal, in addition to these animal sources. Among them are:
Algae: Some varieties of algae are suitable for the extraction of gelatin.
Fruit: Some fruits, like kiwis and jackfruit, are used to make gelatin. The skins of these fruits is used to extract gelatin.
Plant-based gelatins are less frequent than animal-based gelatins, and in some cases, their efficacy may be compromised.

Extraction and Production Process:
Examining and chopping
- Upon arrival at the food processing facility, the animal parts undergo a quality inspection. Rotten components are thrown away. Subsequently, the bones, tissues, and skins are fed into machines that chop the components into tiny bits, with a diameter of about Sin (12.7 cm).
Roasting and degreasing
- high-pressure water sprays are used to wash the animal parts in order to remove any debris. Once the fat level is down to roughly 2%, they are degreased by soaking them in hot water. The cleaned bones and skins are transported by a conveyer belt to a large drier where they are roasted for around 30 minutes at 200° F (100° C).
Treatment with akaline and acid
- For around five days, the animal parts are immersed in vats of lime or another kind of acid or akali. Collagen is released more easily and most of the bacteria and minerals are eliminated during this process. Usually, 4% hydrochloric acid with a pH of less than 1.5 is used for the acid wash. Potassium or sodium carbonate with a pH higher than 7 is used in the alkaline wash.
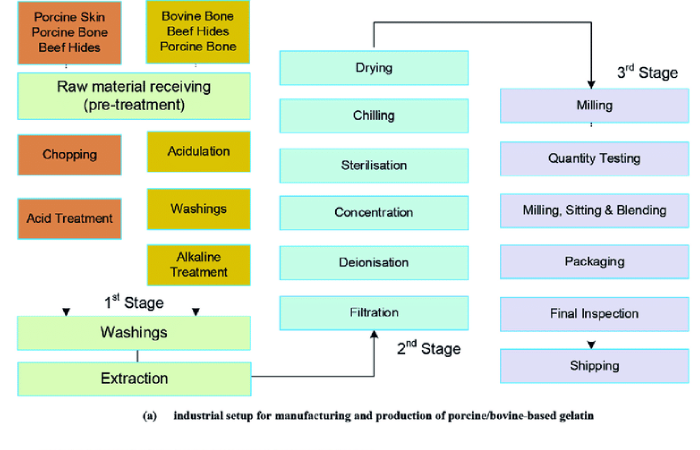
Boiling
- Large aluminum extractors are filled with the bone, tissue, and skin fragments, and they are then heated in distilled water. Workers can remove the liquid that now contains gelatin by pulling on a tube that runs from the extractor. By flash-heating the liquid to roughly 375° F (140° C) for about four seconds, the liquid is disinfected.
Grinding and evaporating
5 The liquid is pumped through filters from the extractor to remove any remaining skin, tissue, or bone fragments. The liquid is pumped from the filters into evaporators, which are devices that separate the liquid from the solid gelatin. After being purged, the liquid is disposed of. Machines go through the gelatin, pressing it into sheets. The gelatin sheets are ground into a fine powder using a grinder, depending on the intended use.
Gelatin's water solubility, ability to produce strong, flexible, and translucent digestible gels and films, and ability to form a positive binding action that is beneficial in the food processing, pharmaceutical, photographic, and paper-making industries are all attributed to its chemical structure.
Color and flavoring
- This is the time to add sweeteners, flavorings, and colorings if the gelatin is going to be used in the food business. The powdered gelatin is thoroughly combined with predetermined proportions of various ingredients.
Storage
Predetermined amounts of gelatin are put into overhead funnels during the automated packaging process, and the gelatin then flows down into bags made of either multiply paper or polypropylene. After that, the bags are vacuum-sealed.
Similarities and differences between traditional and Halal gelatin production.
It is significant to remember that different producers employ different specialized halal gelatin production procedures. Nonetheless, all halal gelatin manufacturing procedures have to abide with the fundamental rules of Islamic law.
Similarities
Raw Materials: Animal bones, skins, and connective tissues are the same raw materials used in the making of both conventional and halal gelatin.
Processing procedures: The fundamental processing steps for the production of halal and conventional gelatin are therefore comparable. To extract the collagen, the raw materials are washed and then cooked. Gelatin powder is created by filtering and drying the collagen.
Differences:
Halal slaughter: In order for halal gelatin to be manufactured, the animals used for the slaughter must follow Islamic law. This means that in order to reduce pain and suffering, the animals must first be stunned before being killed with a sharp knife.
No pork products: It is forbidden to produce halal gelatin using pork products or any other haram material.
Halal certification: A respectable halal certification agency is required to certify halal gelatin. The gelatin has been prepared in compliance with Islamic law, thanks to this certification method.
Ensuring no cross-contamination.
Any step of the gelatin production process, from the extraction of raw materials to the packing of the final product, is susceptible to cross-contamination. To avoid cross-contamination, it is crucial to use stringent food safety procedures at every stage of the production process.
The following are some particular steps that manufacturers of gelatin can take to avoid cross-contamination:
Separation of raw materials: To avoid cross-contamination, raw materials need to be kept apart. Raw hides and bones, for instance, are to be kept apart from other food items in storage.
Detailed cleaning and sanitization: Following every use, all tools and surfaces that come into touch with gelatin should be meticulously cleaned and sterilized. This aids in the elimination of any potentially dangerous microorganisms.
Appropriate staff training: Employees should receive adequate training on cross-contamination prevention techniques and food safety.
Frequent audits: To make sure that their food safety protocols are working, gelatin manufacturers should carry out frequent audits.
- Gelatin manufacturers may contribute to ensuring the safety and superior quality of their goods by putting these precautions into practice.
Hydrolyzed collagen is produced from animal byproducts from the meat industry, such as connective tissue, skin, and bones, or animal remains that have been cleaned by knackers. This process is similar to that of gelatin.
In America, the FDA began monitoring potential instances of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), often known as mad cow disease. The TSE (transmissible spongiform encephalopathy) Advisory Committee assisted with this in 1997. A combination of heat, alkaline treatment, and filtering procedures can help reduce the amount of contaminated TSE chemicals.
But current scientific data does not support the idea that these treatments would successfully eradicate the BSE infectious agent, assuming it were present in the source material," an FDA study from that year said.
The FDA finalized three interim final guidelines on March 18, 2016, with the goal of lowering the possibility of BSE in food intended for human consumption. The final regulation emphasized that "gelatin is not considered a prohibited cattle material if it is manufactured using the customary industry processes specified.
In 2003, the European Union's Scientific Steering Committee (SSC) declared that there is either no risk at all or very little risk connected to bovine bone gelatin.
The 2003 request to remove the skull, brain, and vertebrae of bovine origin older than 12 months from the material used in gelatin was recommended to be removed, according to the European Food Safety Authority's 2006 statement, which also confirmed the SSC opinion and stated that there was little risk of BSE in bone-derived gelatin.
Ethical Consideration
There are no simple solutions to the ethical dilemma of using animal products to produce halal gelatin. Customers should consider all of the relevant aspects, including the welfare of animals, the impact on the environment, and their religious convictions.
Animal Welfare
The welfare of the animals used to make halal gelatin is one of the key issues surrounding it. Animals must be killed quickly and with the least amount of pain and suffering in order to practice halal slaughter. There is proof, nevertheless, that not all halal slaughterhouses adhere to these requirements.
For instance, a 2016 research by Compassion in World Farming discovered that blunt knives, which can cause animals to suffer greatly, were being used in certain UK halal slaughterhouses. Additionally, the study discovered that certain animals were being killed without first being stunned.
It is imperative to acknowledge that these results may not necessarily reflect the majority of halal slaughterhouses. Numerous halal slaughterhouses that adhere to strict moral guidelines exist. When buying halal gelatin products, it's crucial for customers to be aware of the possibility of problems with animal welfare.
Effects On The Environment
The effects of animal agriculture on the environment are a further worry with halal gelatin. Deforestation, water pollution, and climate change are all directly caused by animal husbandry.

Gelatin made with halal ingredients is also produced. The animals raised in factory farms, which are notorious for their negative effects on the environment, are usually utilized to make halal gelatin.
Customers who care about how their food choices affect the environment might want to look into buying halal gelatin products that come from animals produced more sustainably, like on farms that practice regenerative agriculture or free-range farming.
Religion-related views
Halal gelatin is significant to Muslims because it enables them to eat food that conforms to their religious principles. Muslims are obligated by Islam to consume meat that has undergone halal slaughter. This implies that the animal needs to be killed as soon as possible and with the least amount of agony.
Muslims also benefit from halal gelatin since it keeps them from consuming pork-based foods. In Islam, pork is regarded as haram, or prohibited.
The ethics of sourcing animals for Halal gelatin
Numerous contemporary practices have the potential to seriously harm animals and are in conflict with the aforementioned lessons. Animals are frequently treated cruelly both before and during transportation. For several days, some animals are marched on foot. Animals may lose weight and suffer needless beatings during such travel. A lot of creatures travel without food or water.
Animals transported in crammed, poorly ventilated trucks for three or four days at a time suffer needlessly, especially in hot, muggy conditions.Slaughterhouses also have harsh conditions. Animals may be confined with brief tethers in rudimentary facilities that don't provide shade. Animals are frequently hit and beaten at the point of killing in order to force them into the facilities.
Islam's primary teaching on the killing of animals for food is to do it as humanely as possible. Islamic norms regarding the treatment of animals, especially the manner in which they should be slaughtered, are founded on altruism, compassion, and fellow-feeling.
Treatment, slaughter, and processing in accordance with Islamic principles
It is imperative that all Muslims become aware of the Qur'anic and Hadithic teachings about animal welfare. This strategy will undoubtedly have an impact on most Muslims involved in the cattle sector, particularly the butcher, who will be persuaded to treat animals with greater compassion.
Religious organizations and groups must intervene at the highest level in order to do this, as they are best suited to give fatwas or rulings on this matter. Animal abuses and poor procedures during the production of halal meat must be studied, and solutions to enhance animal welfare need to be proposed, including the use of imams' sermons at mosques to raise awareness of animal welfare issues.
Comparison Between The Environmental Footprints Of Traditional vs. Halal Gelatin Production.
Halal and regular gelatin have comparable environmental footprints. These production techniques generate greenhouse gases and other pollutants in addition to requiring land, water, and energy.
The kind of bone and chemicals employed in the two production processes, for example, are two major distinctions that may have an effect on the environmental impact.
Halal gelatin production does not involve the use of chemicals to extract the gelatin from the bones, as does ordinary gelatin production. Since the chemicals employed in the conventional production of gelatin can contaminate the environment, this may also have an effect on the environmental footprint.
It is noteworthy that the environmental impact of conventional and Halal gelatin can be mitigated through the implementation of more economical production techniques and the procurement of raw materials from sustainable sources.
Consumer Rights and Transparency
Consumer trust in the Halal gelatin business can be bolstered by unambiguous labeling and certifications. Customers are more likely to be assured of the items' quality and authenticity when they notice that Halal gelatin products are properly labeled and certified. This may contribute to the growth of the Halal gelatin business and raise demand for Halal gelatin.
The need for clear labeling and certifications
-
Labels should be very meaningful, clear, and descriptive for the consumer's advantage. The origin of the ingredients is typically not listed on the ingredient label.
-
Another major issue for Muslim customers is the presence of hidden substances including transporters, anti-caking agents, processing aids, and incidental ingredients from different sources.

-
For instance, the source of the magnesium or calcium stearates used in the production of candies and chewing gum is never disclosed. Certain European producers can claim to be pure chocolate even though their product contains up to 5% vegetable or animal fat.
-
It is frequently impractical to provide a list of all major and minor ingredients on the label. Product halal certification and appropriate halal labels and logos can clarify the doubts for the consumers.
-
Alcohol needs to be listed as an ingredient on the label if it is a component of the recipe or composition of the food. Alcohol falls under incidental ingredients if it is present in other substances.
-
Certain accidental additions are excluded from the need for food labels since they are present in food at trace amounts and have no functional or technical impact on the product.
-
Halal certification along with appropriate labelling and marks can help address the two labeling issues that Muslims are concerned about: the ingredients that are hidden and the ones that are questioned.
-
Muslims no longer have to commit to memory a list of cryptic E-numbers in Europe or chemical terminology in the United States every time they go grocery shopping thanks to the certification of halal emblem on food goods.
-
However, it should be mentioned that the things that are marked are the only ones that have been verified, certified, and tested to ensure that they are halal.

Why Ethical Consumers, Vegetarians, and Food Scientists Should Care?
Considerations For Ethical Consumers
Buying goods and services that are created in a way that minimizes harm to society and the environment while avoiding goods and services that are thought to have a detrimental effect on either can be referred to as ethical consumerism.
Choosing products that respect animal welfare and sustainability.
High-quality scientific data on each of the many sustainability components is required in order to appropriately take them into account. Decision-making can be done in two ways after information has been gathered.
Comparing the magnitude of each good and negative outcome is one strategy. It is preferable to express each in the same units in order to do this. For instance, ratings for river pollution, water use, greenhouse gas emissions, and animal welfare
Each of the many elements of sustainability should be measured precisely when evaluating a system. Biodiversity, worker satisfaction, land and water use, greenhouse gas production, harmful accumulation of pollutants like nitrogen, welfare of humans and other animals, and the price consumers will pay.
It can be difficult to select goods that uphold sustainability and animal welfare
The majority of consumers believe that standard tier products meet acceptable criteria for animal welfare, and retailers and assurance programs are relied upon to make sure this requirement is fulfilled.
We are aware that consumers value animal welfare highly. Price, however, may have a greater impact at the time of purchase, casting doubt on the idea that buyers are prepared to pay more for goods that prioritize animal welfare.
Customers may claim to be concerned about animal welfare, but the limited adoption of better welfare meat among them shows that they may not be ready to pay more for these high-end goods and will typically choose a less expensive option when it comes to
Here are some recommendations for selecting goods that respect sustainability and animal welfare:
Seek for goods that have certification from reliable agencie: Numerous organizations certify items according to their sustainability and animal welfare requirements. Among these groups are the following:
- The program known as American Humane Certified
- The Worldwide Animal Alliance
- The Alliance for Rainforest
- The Council for Marine Stewardship
- The Foundation for Fair Trade
Purchase goods from nearby and regional vendors: Purchasing goods from nearby and regional vendors lessens the influence that food production and transportation have on the environment. Additionally, it supports regional economies and companies.
Select goods that are manufactured using sustainable materials: Look for ingredients that are produced sustainably while making product selections. Consider products that use resources from sustainable fisheries or those manufactured with organic ingredients.
Vegetarians Concern
The effects of halal gelatin production on the environment worry some vegetarians. A significant quantity of land, water, and energy are needed for the rearing and killing of animals for halal gelatin. In addition, it emits additional pollutants including greenhouse gasses.
Understanding Gelatin
Gelatin is most commonly found in gummies (including gummy vitamins), marshmallows, candy corn, Panna cottas, fruit snacks, and some pastry creams, such as Bavarian creams, puddings, custards, and mousses. However, there are some vegan exceptions or merely unintentionally vegan-friendly one-offs.
Jell-O is basically gelatin that has been sweetened and flavored. Although it's not as popular, gelatin can also be used as a stabilizer in some ice cream recipes.
Gelatin is frequently used in the production of popular goods including Jet-Puffed, Peeps, Altoids, Starburst, Jell-O, Lifesavers, Haribo, Trolli, and frosted cereals like Frosted Mini-Wheats. For any food with a squishy, gummy, or jiggly texture, it's always a good idea to read the ingredient label unless the container specifically states that it's "plant-based" or "vegan."
Alternatives For Vegan Consumers
Not everything that can set a pastry cream into a thick and silky pudding or turn a sweet gummy is made from animal gelatin. These challenging textures have also been successfully recreated using cornstarch and agar agar (an algae-based substance found in the seaweed department).
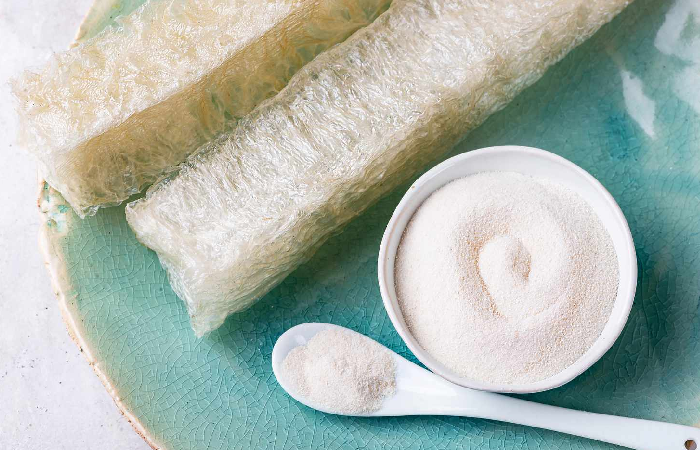

Agar agar and cornstarch get activated when mixed with a hot liquid, just like gelatin does. Agar agar sets at room temperature and thickens liquids just as quickly as cornstarch, taking only a few minutes to thicken.
Food technology firms are also developing gelatin products that don't involve animals. A 2015 Silicon Valley firm called Geltor is spearheading the effort to create vegan proteins that mimic the properties of animal products like gelatin and collagen.
The business raised $91 million in 2020 to support this endeavor, and it currently provides four solutions for usage in food, skincare, and cosmetics on a commercial basis.
Role Of The Food Scientists
Due to its growing global popularity, halal gelatin is a product that food scientists should be concerned about. More ethical and sustainable production techniques must be developed as the market for halal gelatin grows.
New techniques for making halal gelatin that are considerate of vegetarians and the environment can be developed by food scientists. Additionally, they can endeavor to guarantee accurate labeling of halal gelatin, enabling vegetarian customers to make knowledgeable decisions.
Here are some cutting-edge techniques used to produce halal gelatin
Fish scale-derived gelatin: Scientists at the University of Putra Malaysia have created a process for turning fish scales into gelatin. Compared to conventional techniques, this approach of making gelatin from bones and hides is more effective and sustainable.

Seaweed-derived gelatin: The University of Indonesia's researchers have created a process for making gelatin from seaweed. Compared to conventional procedures, this approach to gelatin production is also more effective and environmentally friendly.
Microbial fermentation gelatin: The University of California, Berkeley researchers have created a process for microbial fermentation that yields gelatin. There is no need for animal killing or the usage of components obtained from animals in this process.
Is Crab Halal?
Crabs are among the many marine animals that are commonly found in the world's seas and oceans. They are rich a rich source of protein and are eaten globally.
The topic of whether or not "crab" is halal cuisine has gained popularity as more and more individuals adopt halal diets and convert to Islam. It is important for Muslims to know what foods comply with and which do not with the Islamic dietary code.
It is significant to remember that certain foods and animals can be regarded as dubious or questionable in addition to being allowed (halal) or forbidden (haram).
This suggests that the food in question is probably neither obviously halal nor haram. It is best in these situations to seek the advice of religious authorities in order to better understand whether the food is permissible.
Seafood in Islamic Dietary Laws:
General permissibility of seafood
The Islamic dietary regulations restrict some types of fish for several reasons. One explanation for this is that these creatures are regarded as scavengers and might consume other, dirty animals. These creatures might reside in environments that are seen as dirty, which is another explanation.
Muslims who adhere to Islamic dietary regulations take care to consume only permitted fish. Additionally, they take care to guarantee that the seafood is cooked in a hygienic and clean manner and that it is caught in a humane manner.
Differences in interpretation among Islamic scholars
According to their interpretation of Quran 5:96, most Islamic schools allow the eating of game of water, which includes fish and other sea creatures.
-
However, the Hanafi school of Islamic jurisprudence prohibits the eating of any seafood other than true "fish" and views other sea creatures, including crustaceans, as makruh.
-
While many scholars do agree that crocodiles, crabs, lobsters, and other mollusks are not actual "fish," some Hanafi scholars dispute over whether prawns and shrimp comprise a true fish.
-
Al-Hindiyya al-Fatawa, 5/289–291, Sana'i al-Bada’i, 5/35–39, and Muhtar al-Radd, 304–308.
-
Shia hadith forbids eating any kind of eel, even those found in freshwater and the ocean.
-
Seahorses, lobsters, and crabs are among the seafood varieties that are allowed, according to the Maliki school of thought.
-
The Shafi school of thought states that while hermit crabs, crocodiles, and sea snakes are prohibited, all fish that isn't venomous, such as puffer fish, rock fish, and the like, is acceptable.
-
It also states that any crustacean that doesn't live on land, such soft-shell crabs and lobsters, is allowed.
The Hanbali school of thought holds that crabs are prohibited for the same reasons as the Hanafi and Shafi'i schools do.
They contend that the only marine creatures that are deemed halal are fish, and a crab is neither a fish nor a scaled animal.
The Maliki school of thought adopts a more liberal stance and permits the eating of crabs in dire circumstances.
This perspective holds that eating crab can stave off hunger since the need to survive outweighs the limits of Islamic dietary regulations.

The Crab Debate
One of the most popular seafoods is crab. Worldwide, a lot of people enjoy eating crab. But when it comes to the Muslim community, we wonder—or Muslim individuals wonder—if crab is halal or haram in Islam
Debate In Favour Of Crab Being Halal
Because crabs are aquatic animals with exoskeletons, they are comparable to fish, according to academics who support crabs being considered halal. They contend that it qualifies as halal fish.
-
They also take into account this passage from the holy Quran that Allah SWT says.
-
"(The hunt for) water game and using it as food is lawful for you; it is for the benefit of yourself and other travelers." [Quranic verse 5:96]
-
He is the one who subdued the sea so you might obtain the jewelry you wear and eat its delicate meat. Qur'an 16:14.
-
According to a hadith, several of the Prophet's (peace be upon him) companions inquired about eating crabs. "Eat them and mention the Name of Allah when you start to eat them," declared the Prophet (pbuh).
-
"Every moving creature in the sea is halal and permitted for you to eat, and fish in the sea are like sheep among cattle," declared the Prophet (pbuh).
-
These hadith and verses from the holy Quran were used as proof by the scholars who support crab halal. "It is He who has made the sea subservient so that you can eat from it tender meat and extract ornaments that you wear," Allah SWT said in reference to these verses. Qur'an 16:14.
Raesons For Crab Being Haram
In support of their claim that crabs are haram, academics note that they may live both on land and in water.
-
They contend that the lack of scales distinguishes crabs from fish, making it unlawful to eat crab.
-
Islamic law prohibits the consumption of crab, as per Hanafi jurisprudence.
-
According to certain academics, eating crab and lobster is forbidden.
-
They believe that only fish with scales and fins are acceptable, based on marine life.
-
Because they lack scales and fins, crabs are classified as crustaceans and are therefore not pure in Islamic law.
-
Therefore, one group of Muslims considers crab to be haram, or forbidden.
Practical Recommendations On Eating Crab
It is imperative that customers seek advice from local academics or adhere to their particular school of thought when making decisions on their consumption of seafood.
Scholars in the area are knowledgeable about Islamic law and can offer advice on the particular standards for halal fish. Additionally, they can assist customers in determining which seafood is acceptable and which is not.
Customers can seek advice from local academics or adhere to a certain school of thought by:
-
visiting an Islamic center or mosque in the area.
-
reading Islamic law-related books and articles.
-
attending sermons and lectures delivered by Islamic experts.
-
utilizing social media and other internet tools like webpages.
Different schools of thought may interpret Islamic law differently, thus it's critical for customers to heed the advice of the school of thought that best suits them.
Conclusion
It is clear from the previous description that different researchers have different opinions about eating crabs. Ultimately, it is up to each individual whether or not to consume shellfish like crab.
If you want to be extra cautious about this, you might speak with someone who has a lot of knowledge or simply stay away from eating crab in favor of other seafood options.
We have discussed in detail about halal gelatin and the alternate sources of gelatin. Agar Agar as a vegan option for vegetarians and also innovations in production of halal and vegan gelatin.
In conclusion, not all types of gelatin are halal but you can find bovine gelatin halal, beef gelatin halal, and fish gelatin halal. These options are available in the market and most of manufacturers in the market have halal certified gelatin.
Reading And References
Here are some reading material for crab as halal:
- Islamic Ruling on Crab by Mufti Muhammad Taqi Usmani
- Is Crab Halal? by Dr. Muhammad Solaiman Ghani
- The permissibility of eating crab by Dr. Zaghloul al-Najjar
Here are some reading materials available for halal gelatin:
- The Halal Food Handbook by Muhammad Abdul-Rahman Yusuf
- Halal Food Production by Yusuf Khan and Munir Ahmad
- The Halal Food Guide by the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America
- Halal Gelatin: A Review of Its Production and Uses by Muhammad Abdul-Rahman Yusuf
- Gelatin: A Review of Its Production, Properties and Uses by Munir Ahmad
References
https://wehalal.co/blog/is-crab-halal-or-haram/
https://theislamicinformation.com/fatwas/is-crab-halal/
https://halalguidance.com/is-crab-halal/
https://www.hearthyfoods.com/blogs/news/benefits-of-gelatin
https://vegnews.com/vegan-guides/gelatin-vegan




